Pymetrozine - Alternatives, Pros and Cons
Pymetrozine insecticide is key for sucking pest control, but resistance is rising. Learn more about pymetrozine pros, cons, and viable alternatives.

Pymetrozine is a selective insecticide agent used to control sucking pests, such as aphids, whiteflies, and planthoppers, on crops including rice, vegetables, cotton, and ornamental crops. It works by disrupting the feeding behavior of the pests in a way that they soon cease to feed and starve. Although the method is effective, resistance selection and special crop or regulatory demands have prompted the search for chemical alternatives capable of offering similar pest control.
Looking for Reliable Pymetrozine? Request a Sample
Alternatives to Pymetrozine
1.Imidacloprid
A neonicotinoid insecticide known for its systemic activity and broad efficacy against sap-sucking pests like whiteflies, aphids, and leafhoppers.
- Pros:
- Strong knockdown effect and longer residual control.
- Versatile application in multiple cropping systems.
- Cons:
- High resistance development among pest populations.
- Environmental concerns, especially impacts on pollinators.
2.Thiamethoxam
Another neonicotinoid with systemic activity is used against similar pests.
- Pros:
- Rapid activity and effective control.
- Available in various formulations for soil, foliar, and seed applications.
- Cons:
- Resistance issues similar to imidacloprid.
- Regulatory restrictions due to environmental risks.
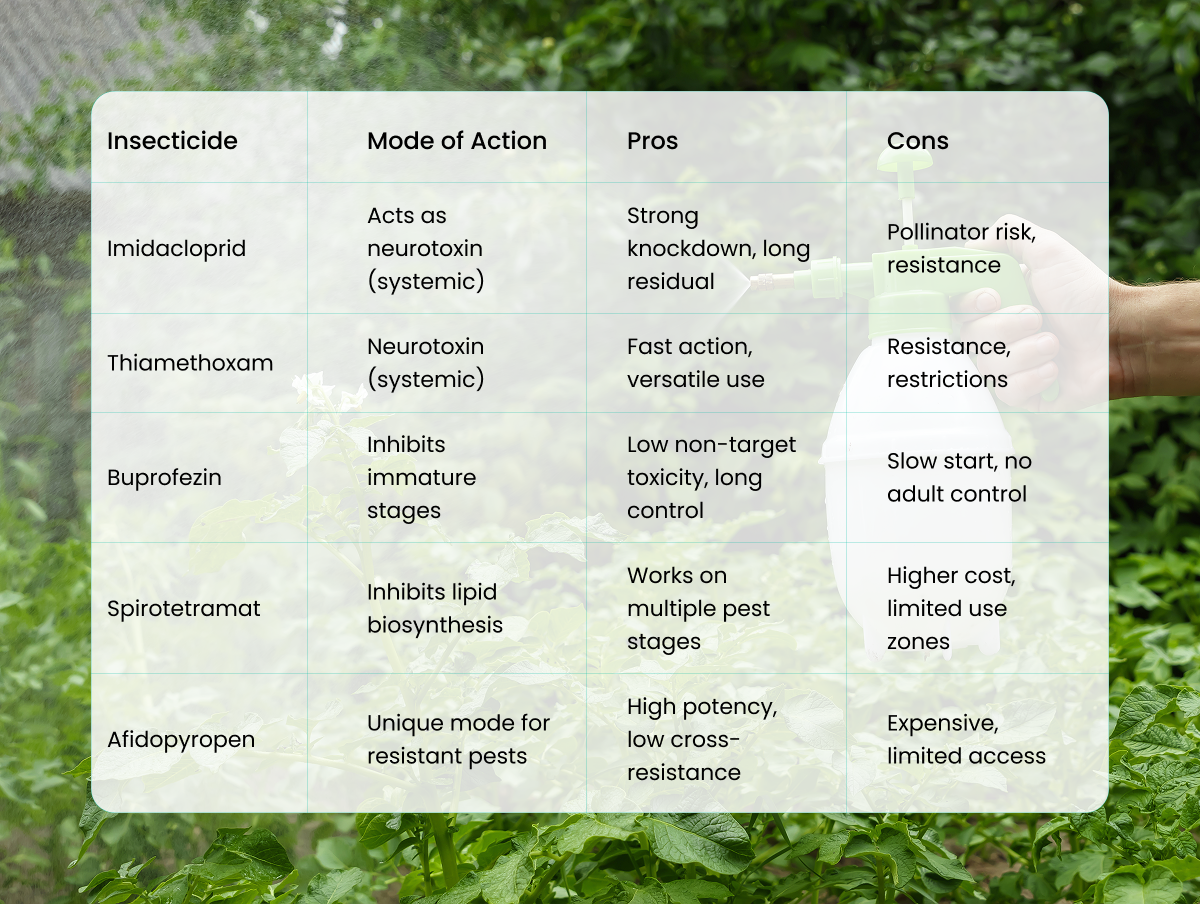
3.Buprofezin
An insect growth regulator (IGR) targeting immature stages of sucking pests.
- Pros:
- Effective for long-term pest suppression.
- Lower non-target toxicity.
- Cons:
- Slower initial knockdown, requiring integration with faster-acting insecticides.
- Limited control over adult pests.
4.Spirotetramat
An active ingredient with systemic and multi-site activity, inhibiting lipid biosynthesis in pests.
- Pros:
- Effective on multiple stages of pests.
- Lower resistance risk due to novel mode of action.
- Cons:
- Cost may be higher compared to traditional insecticides.
- Restricted use in some regions.
5.Afidopyropen
A newer insecticide effective against resistant whitefly populations with a different mode of action than pymetrozine.
- Pros:
- Excellent potency against resistant pests.
- Limited cross-resistance with other insecticides.
- Cons:
- Limited availability and higher price point.
- Requires careful resistance management.
Conclusion
Although Pymetrozine still has its role to play in controlling piercing and sucking pests, problems of resistance and changes in regulations have forced alternative use. Neonicotinoids, such as imidacloprid and thiamethoxam, provide high potency but have environmental and resistance issues. New chemistries such as spirotetramat and afidopyropen, and insect growth regulators offer alternatives that have a promising future with an alternative mode of action essential to integrated pest and resistance management strategies. The correct choice is determined by the type of crop, the pressure of pests, the environment, and the regulatory approvals.


